Disclaimer: This post may contain affiliate links. For more information, please visit our Disclaimer Page.
Introduction
“The Lean Startup” by Eric Ries is a highly influential book that has changed how entrepreneurs approach the startup world.
This book’s main idea is to revolutionize how companies approach value and growth hypothesis discovery and validation. The aim is to turn a company’s vision into a feasible business model through a scientifically rigorous method.
To achieve this, the Lean Startup methodology focuses on creating a minimum viable product and gathering customer feedback to enhance it. Publishing a preliminary version of a functioning product often reveals valuable insights and ideas that would have gone unnoticed otherwise. It enables a more personalized final product.
By embracing a scientific approach to business management, Lean Startups experience faster delivery of products to customers and growth acceleration. The Lean Startup process teaches a systematic approach to innovation, guiding companies to adapt, evolve and persist for maximum business expansion.
Let’s dive in a little deeper!!!
“The Lean Startup: A Different Approach to Entrepreneurship”
Lean Startups’ embody a philosophy and a method for streamlining processes, avoiding waste, and efficiently transforming ideas into successful products and businesses. Its central tenet is the Build-Measure-Learn cycle, where customer feedback and testing drive continuous improvement and informed decision-making.
Building a Culture of Innovation with the Lean Startup Methodology?
Startups are distinctive entities that stand out from the rest, characterized by their elevated level of risk. The reason behind this is their innovative approach to problem-solving.
In response to his failed attempts at launching a startup, Eric Ries penned “The Lean Startup” to help companies reduce their risk through implementing MVP, systematic experimentation, regular feedback collection, adaptive problem-solving ability, and a continuous drive for improvement.
The Lean Startup method embodies creating a successful business with maximum efficiency without wasting unnecessary time and resources.
MVP Definition
The Minimum Viable Product, or put, the “minimum working product,” embodies minimalism with functionality. It strives to fulfill customer demands with the bare minimum and gather crucial customer feedback to refine the offering.
With customer satisfaction as the ultimate goal, feedback allows companies to decipher what works and what doesn’t, enabling them to navigate toward creating unparalleled value.
The 5 Principles of the Lean Startup Method
Eric Ries established five principles of the Lean Startup method. These are the foundations he built his theory, and I relate them below.
Entrepreneurs are Everywhere: The spirit of entrepreneurship knows no bounds. It transcends backgrounds and fields, fueling the drive and ambition of individuals from all walks of life to turn their ideas into realities.
Validated Learning: The key to success for entrepreneurs lies in validating their assumptions through ongoing experimentation and learning. By embracing a trial-and-error approach, they gain invaluable insights and are better equipped to chart their course to success.
Innovation Accounting: Metrics and experiments are indispensable tools for measuring progress and success in entrepreneurship. By embracing innovation accounting, entrepreneurs are empowered to track their progress and make informed decisions.
Build-Measure-Learn: At the heart of the Lean Startup methodology lies the “build-measure-learn” feedback loop, an iterative process that drives continuous improvement and fuels success.
Flow: A successful startup prioritizes creating a steady flow of customer value. By focusing on the needs and wants of their customers, entrepreneurs can build businesses that survive and thrive.”
“The problem with entrepreneurship is that we often work too hard to produce high-quality products that nobody wants.”
Eric Ries
Lean Startup: How it Works
The operation of the Lean Startup method is a continuous cycle composed of the construction, measurement, and learning phase, or the so-called build-measure-learn cycle (build-measure-learn).
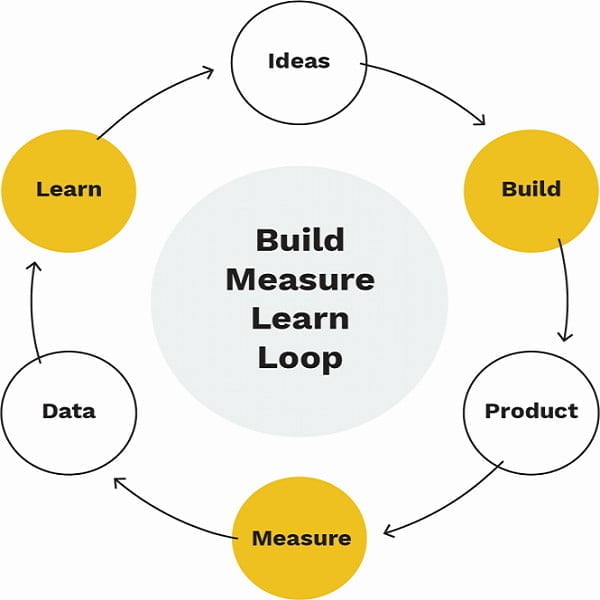
Lean Startup Canvas
The Lean Startup Canvas is a redefinition of the canvas by Ash Maurya.
The differences between the original Canvas business template and this one are:
- Partners / Problem: we must establish the three priority problems we intend to solve instead of partners.
- Key Activities/Solution: One needs to understand solutions to established problems instead of activities.
- Features/Metrics: After that, you must identify the metrics to establish whether the business model is validated.
- Customer Relationship / Unfair Advantage: finding a competitive advantage over competitors.
- Value Proposition / Unique Value Proposition: What is the one reason why a customer should prefer you? What sets you apart?
In conclusion, the Lean Model Canvas focuses on the problem and the solution because they are considered more important than the partners. In addition, the UVP (Unique Value Proposition) is also fundamental, as it is better to focus little but at the beginning.
Examples of Lean Startups
Now let’s see some examples of successful Lean Startup companies.
Dropbox
Dropbox is a popular program run by a Californian company and is a classic example of a Lean Startup.
The famous San Francisco – based file hosting service initially hit the market with a video MVP. Thanks to the feedback and comments obtained, the software was developed and modified, following the indications of the consumers.
The result?
Today, it has around 500 million users worldwide, and most people use it to transfer and sync their large files.
Buffer
Buffer is a fantastic app that schedules all your social posts and quickly organizes your accounts. Joel Gascoigne, the founder, created a basic landing page with a “Plans & Pricing” button to see if consumers wanted his product. This work of his represents a clear example of the Lean Startup method.
The goal was to see if the button was clicked. He later integrated three pricing proposals and noticed people clicked on packages and ordered.
Airbnb
Airbnb’s ascent to the top of the travel industry was fueled by its adoption of the Lean Startup methodology. This approach entails starting small, with a minimal but functional version of a product (in this case, the Airbnb platform), and iteratively improving it based on customer feedback.
By taking this cost-effective route, Airbnb validated its concept and fine-tuned its platform with lightning speed, propelling the company to the heights of success it enjoys today as a multi-billion dollar behemoth.
Zappo
Zappos’ Lean Startup Journey: From Small Online Retailer to Billion-Dollar Empire
Zappos started small, leveraging the Internet’s reach to expand its customer base as an online shoe retailer. But, driven by the Lean Startup methodology, the company continued growing.
By continually taking customer feedback into account and improving its product offerings and customer service, Zappos blossomed into a billion-dollar behemoth, a shining example of the power of the Lean Startup approach.
Advantages
Why Use the Lean Startup Method
Numerous reasons lead more and more startups to approach this technique. The advantages of the Lean Startup method are:
- client-based startup development
- constantly present customer feedback
- work with constant dynamism
- Enter a market with growth potential
- join a niche market before the competition
- develop technologies that reflect customer needs
- definition of a business model
- creation of a Minimum Product (MVP) and continuous testing
- adapts quickly to changes and reassures investors
Conclusion:
“The Lean Startup” by Eric Ries has shattered traditional methods of building startups with its novel concept for startups’ success. The approach’s core lies in rapidly creating and testing a minimal viable product with potential customers, reducing uncertainties, and affirming ideas. By embracing innovation and relying on data-driven progress, startups enhance their odds of sustained success. If you’re an entrepreneur to launch a startup, “The Lean Startup” is an absolute must-read that will revolutionize your perspective and approach to building and managing your startup.
F.A.Q. about “The Lean Startup” by Eric Ries
What is the Lean Startup Methodology?
The Lean Startup Methodology is a trailblazing approach to starting and running startups, introduced by Eric Ries in his book “The Lean Startup.” It prioritizes creating and rapidly testing an MVP with potential customers to validate ideas and reduce risk.
Why is “The Lean Startup” by Eric Ries Significant?
“The Lean Startup” has significantly impacted the entrepreneurial arena with its novel approach to launching startups. Rather than spending years developing a potentially unsuccessful product, the Lean Startup Methodology prioritizes testing an MVP with customers and pivoting quickly if needed. This minimizes risk and conserves resources.
How Does the Lean Startup Methodology Foster Innovation?
The Lean Startup Methodology cultivates a culture of innovation by embracing failure as a learning opportunity and promoting calculated risk-taking. This fosters a flexible and adaptable startup, crucial for success in the ever-evolving startup landscape.
“The Lean Startup” Book Quotes
“Fail fast, fail often: The only way to win is to learn faster than anyone else.”
“Entrepreneurship is not just a job; it’s a way of life.”
“Innovation is not about saying yes to everything; it’s about saying NO to all but the most crucial features.”
“Validated learning is the process of demonstrating empirically that a team has discovered valuable truths about a business.”
“The only way to win is to learn faster than anyone else.”
“Focus on what’s essential. Don’t get distracted by the shiny new objects.”
“Growth is not merely a quantitative improvement, but a qualitative leap.”
“The goal of a startup is to figure out the right thing to build—the thing customers want and will pay for—as quickly as possible.”
Disclaimer: This blog post is a summary or resume of the book and is not intended to dispense the reading of the original book. This post aims to provide a general overview of the book’s main ideas and themes and encourage readers to read the complete book to gain a deeper understanding of the material. The information presented in this post is intended to be something other than a substitute for the original book and should be used as a supplement to, not a replacement for, the entire book. We strongly encourage readers to read the complete book to benefit from its ideas and teachings fully.











